|
Topic 1: Structures of the Hair
Formation
of the Hair Bulb
While
a baby is a fetus, the hair follicle is formed in the upper layer of the
skin from a cluster of cells. These cells are called the primitive hair
germ. Primitive hair germ cells get their nourishment by working their
way down into the dermal layer of the skin. This cluster of cells creates
a follicle as they pull the upper layer down in their search for nourishment,
thereby creating a pocket known as the root sheath. Out of this sheath
the hair will grow. Hair grows from stem cells. These cells grow directly
under the oil (sebaceous) glands. As the cells continue to grow, the nucleus
of the cells disappears and the cells become keratinized.
What
Gives Hair its Shape
The
shape of the hair shaft is determined by the shape of the hair follicle.
People with straight or wavy hair have typically round or oval shaped
hair follicles. The hair follicle of hair that is curly or overly curly
is elliptical in shape.
Structures of the Hair
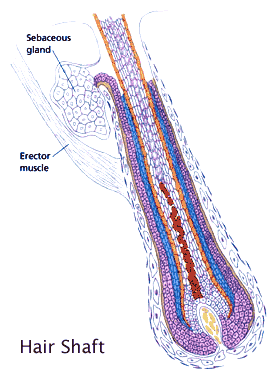
Sebaceous
Glands
Other
changes take place in the hair follicle. Small, sac-like glands appear
on the upper part of the follicle. One of the glands is the sebaceous
gland. The function of these glands is to produce a substance called sebum.
This substance is secreted into the hair follicle to lubricate and condition
the hair and the skin. Sebum is a mixture of fats, proteins, cholesterol,
alcohol and salts. When sebum mixes with the perspiration on your skin,
it forms what is called the "acid mantle". This acid mantle is what protects
your skin from bacteria and infections.
Arrector
Pili Muscle
Just
below the sebaceous gland, in the follicle is the arrector pili muscle.
This is the muscle that causes you to have "goose bumps" or causes your
hair to stand on end when you are cold or scared.
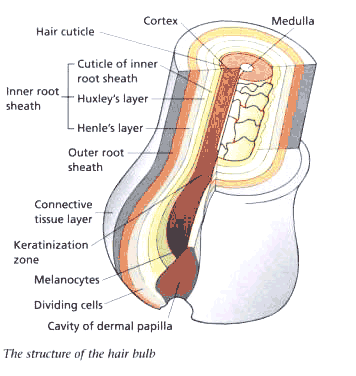
Dermal
Papilla
A
small cone-shaped elevation is located at the base of the hair follicle.
This is the dermal papilla. The dermal papilla fits into the hair bulb
and contains the blood and nerve supply, which nourish the cells around
the hair bulb for growth. These cells are the germinal matrix cells. The
germinal matrix area is where mitosis takes place and produces the keratin,
which forms the three layers of the hair.
Growth
Cycles of the Hair
Hair,
like most living things goes through cycles of growth. Hair goes
through three cycles which are repeated over and over. The three cycles
are the anagen, catagen and telogen phase. The gowth phase of hair is
known as the anagen phase. In this stage the stem
cells manufacture new keratinized cells and the hair grows faster than
any other time. This stage lasts about four years. In the catagen
phase of growth the follice goes through many changes. During this
stage, the follicle canal shrinks,the hair bulb disappears and the hair
root becomes rounded. The melanocytes stop producing color pigments
and the dermal papilla shrinks. During this phase the follicle is preparing
for new growth. This stage lasts from two to three weeks. The resting
stage of hair growth is called the telogen phase. It is during
this stage that the old hair shaft is shed. Often the hair bulb is still
anchored to the follicle walls. When this happens the hair remains in
place until the anagen stage and then it is pushed out. This resting phase
last for approximately one hundred days. The cycle repeats itself over
and over every four to five years.
Glossary
of Terms
Arrector
Pili Muscle - small involuntary muscle fibers in the skin
attached to the base of the hair follicle.
Dermal
Papilla - an elevation of the projecting corium into the
overlying epidermis.
Follicle
- a small secretory cavity or sac; the depression in the skin containing
the hair root.
Germinal
matrix - an area of reproducing cells situated around the
papilla at the base of the hair bulb.
Hair
bulb - the lower extremity of the hair.
Sebaceous
glands - oil glands of the skin connected to hair follicles
|

